Symptoms of prostatitis can be detected a few days after the onset of the disease. Depending on the age, individual condition of the patient and other nuances, the disease can appear clearly or proceed more quietly. Early access to the doctor and timely diagnosis guarantee successful treatment, absence of complications and relapses.

Risk group
Inflammation of the prostate in men is diagnosed more and more often. The essence of the disease is simple. The gland, which is normally very small, grows dramatically, compresses the urinary tract and seminal ducts, causing problems with urine output and normal ejaculation. There are many reasons for the appearance of the disease. The following patients are at risk:
- middle age and old age;
- overweight and obese;
- smokers and alcohol abusers;
- who have had diseases of the urogenital area (urethritis, cystitis, orchitis, balanitis, balanoposthitis, pyelonephritis);
- having an irregular sex life;
- practicing coitus interruptus as the main means of contraception;
- undergoing treatment with powerful drugs (hormonal agents, antibiotics).

A few decades ago, symptoms of the disease were observed in middle-aged and elderly patients. But today, the disease is more and more common among active young people who do not have any particular health problems. Urologists distinguish 4 types of prostatitis: acute and chronic infectious, non-bacterial, prostatodynia.
The acute infectious form is more common in young, sexually active men. The cause of the disease is bacteria that have entered the urethra and urethra. The source of infection is often the causative agents of sexually transmitted diseases: streptococci, gonococci, pale spirochetes, Trichomonas, chlamydia. In some cases, bacteria enter the urethra from the rectum. This happens with insufficient hygiene of the genitals. In the absence of adequate treatment, acute infectious prostatitis can become chronic. It is characterized by alternating periods of rest with a sudden deterioration of well-being. As the disease progresses, attacks become more frequent and last longer.
The onset of the disease: how to determine it
The first symptoms of prostatitis are easily confused with the manifestations of other diseases. That is why patients do not rush to the doctor, taking sedatives or antipyretics themselves. One sign that should alert you is going to the toilet too often. The man begins to notice that little urine is released, becomes dark in color or becomes almost transparent. Gradually, the process of passing urine becomes painful, itching and burning are felt in the urethra, the external genitals are irritated and reddened.

Another characteristic manifestation is a constant feeling of fullness in the bladder. The enlarged gland presses on the ureter, urine is secreted drop by drop or flows spontaneously. There may be incontinence at night and pus, ichor or mucus may be released from the urethra.
Almost at the same time, disorders of sexual function are observed. An enlarged prostate blocks the flow of testosterone, a man notices a decrease in sexual desire, premature ejaculation, deterioration of erection.
Against the background of the inflammatory process and failures in the genital area, the patient becomes irritable, irritable, outbursts of aggression or a depressed, depressed mood are possible.
Fatigue is very common. An active person gets tired quickly, experiences drowsiness, but even a long sleep does not bring joy. Decreased efficiency, the body cannot resist infections. As a result, even a common cold ends with complications that further worsen the patient's condition.
Signs and manifestations

Symptoms of prostatitis in men can be visible or hidden. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the body, the presence or absence of other chronic diseases, age and other important points. Usually the first characteristic manifestations occur a few days or weeks after the onset of the disease. This includes:
- repeated false urge to urinate;
- pain in the urethra during and after urination;
- local edema in the genital area;
- the feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied;
- problems with urination;
- dull pain in the lower abdomen;
- discomfort in the scrotum and lower back;
- general illness;
- short-term increase in temperature.
With prostatitis, the patient may have problems with sleep and appetite, often constipation, alternating with diarrhea. The main symptoms of prostatitis, characteristic of the non-bacterial form, appear and disappear, become more pronounced or weaken significantly. With chronic inflammation of the prostate, the characteristic signs are not felt for a long time.
They can be so lethargic that a man does not show concern, attributing the deterioration of health to a cold, stress, fatigue at work. According to statistics, almost a quarter of patients do not feel discomfort within a few months after the onset of the disease.

Acute infectious prostatitis, the symptoms of which become apparent after a few days, is manifested as a sharp increase in temperature, burning and pain in the urethra, a constant desire to visit the toilet. The patient experiences chills and fever. Possible problems with stool. In the inflammatory process, tissues are loosened and easily damaged. The patient urges him to go to the toilet, the stools are compressed and barely pass through the rectum. In severe form, the development of hemorrhoids, the appearance of cracks in the rectum and other unpleasant consequences are possible.
A striking symptom of acute prostatitis is the appearance of traces of blood and pus in the urine. Urine becomes cloudy, acquires an unpleasant smell. Urine comes out drop by drop or remains for several hours, causing severe swelling. Everything speaks of an acute inflammatory process. At the first signs of prostatitis, it is recommended to contact a therapist who will refer you to a urologist.
Prostatodynia and its symptoms
Prostatodynia is a non-inflammatory form of prostatitis. It occurs in 30% of middle-aged and older men. The disease continues in a latent or acute form, with a number of characteristic signs of non-infectious prostatitis.
The main difference of this form of the disease is the absence of high temperature, edema, suffocation. At the same time, the patient constantly feels pain of a very different nature: pulling, aching, throbbing. It can be located in the perineum, extending to the lower back, legs, lower abdomen, scrotum or penis. Pain appears at rest or during overload; Blockades of sedatives or the use of powerful drugs can relieve an attack. Antibiotics do not help, since the inflammatory component is missing.
Prostatodynia is characterized by problems with urination. Among them:
- slow flow;
- drip flow;
- incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- frequent false alarms;
- dysuria (complete lack of urine).
How to make a diagnosis
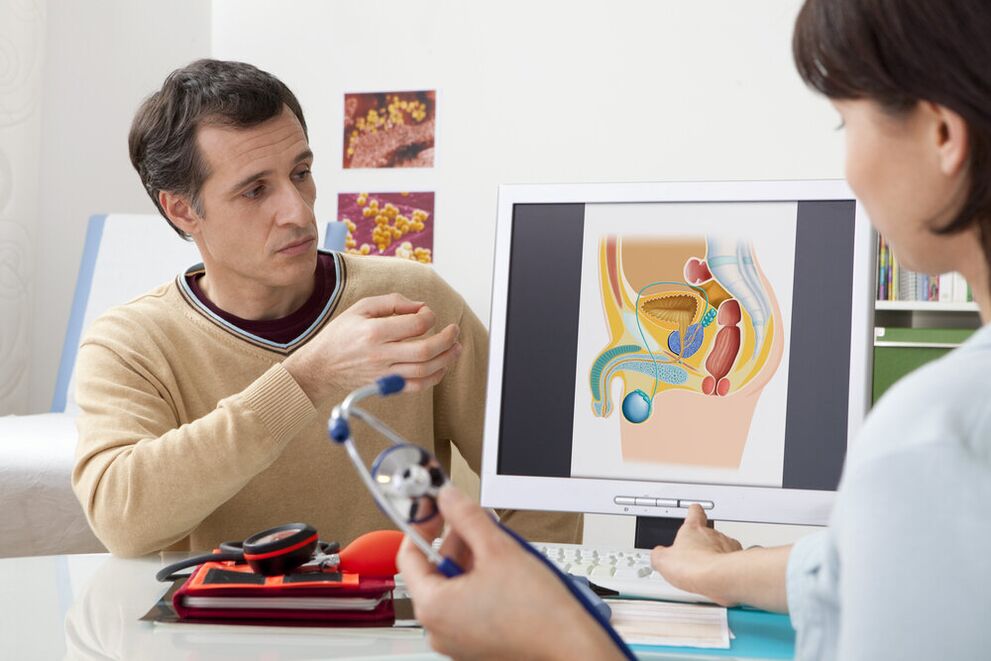
With prostatitis of any nature, the main thing is not to delay treatment for a long time. Only a urologist is able to understand what forms the disease will take and what to choose for a quick recovery. The peculiarity of inflammation of the prostate is that the disease is easily confused with other diseases.
For example, problems with urination are characteristic of chronic or acute urethritis or cystitis. Pain in the lower abdomen and the appearance of blood in the urine can signal pyelonephritis.
Finally, a general deterioration of well-being is characteristic of a whole list of diseases, from the banal flu to colon cancer.
A series of tests and an ultrasound examination to assess the state of the prostate will help to avoid mistakes and improper treatment.
If the cause of the disease is a urinary tract infection, it is necessary to eliminate it and only then proceed with the elimination of prostatitis symptoms.
A few decades ago, it was believed that the disease is typical for older men, but today many young people who lead an active lifestyle also suffer from this disease. Once you have found the characteristic symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor who will establish a diagnosis and choose the appropriate treatment.